Server Virtualization

Virtualization has had an incredible impact on the use of IT as a means to helping companies achieve their business goals. The power of software-defined architectures frees us from many of the physical constraints of hardware and allows us to optimize all the resources we have at our disposal, making the use of IT much more economical, scalable, and flexible. The benefits afforded through virtualization are so great that its popularity has now expanded from its initial server implementations to storage and networking systems.
Storage virtualization is the pooling of physical storage from multiple storage devices into what appears to be a single storage device - or pool of available storage capacity - that is managed from a central console. The technology relies on software to identify available storage capacity from physical devices and to then aggregate that capacity as a pool of storage that can be used in a virtual environment by virtual machines (VMs).
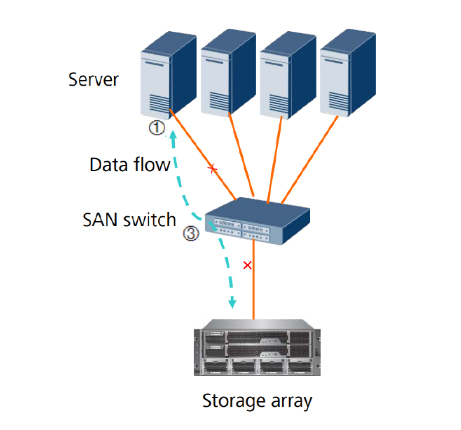
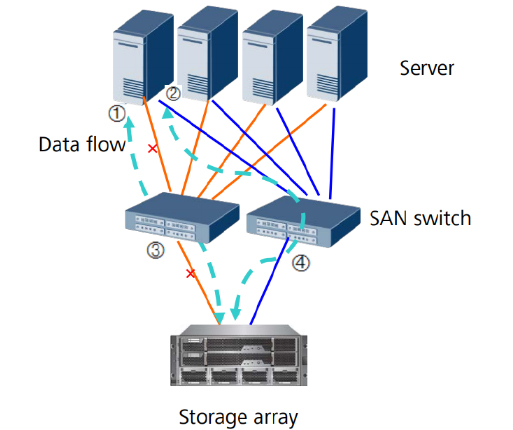
The virtual storage software intercepts I/O requests from physical or virtual machines and sends those requests to the appropriate physical location of the storage devices that are part of the overall pool of storage in the virtualized environment. To the user, virtual storage appears like a standard read or write to a physical drive.
Even a RAID array can sometimes be considered a type of storage virtualization. Multiple physical disks in the array are presented to the user as a single storage device that, in the background, replicates data to multiple disks in case of a single disk failure.
Types of storage virtualization
In simple terms storage virtualization is the process of representing physical storage in the logical form to any server
There are two basic methods of virtualizing storage: file-based or block-based. File-based storage virtualization is a specific use case, applied to network-attached storage (NAS) systems. Using the Server Message Block (SMB) or Network File System (NFS) protocols, file-based storage virtualization breaks the dependency in a normal NAS array between the data being accessed and the location of physical memory. This enables the NAS system to better handle file migration in the background to improve performance.
Block-based or block access virtual storage is more widely applied in virtual storage systems than file-based storage virtualization. Block-based systems abstract the logical storage, such as a drive partition, from the actual physical memory blocks in a storage device, such as a hard disk drive (HDD) or solid-state memory device. This enables the virtualization management software to collect the capacity of the available blocks of memory space and pool them into a shared resource to be assigned to any number of VMs, bare-metal servers or containers.
