Server Virtualization

What is server virtualization?
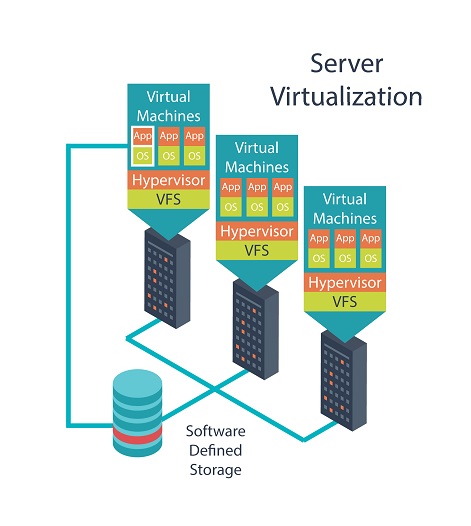
Server virtualization is a technology that allows for the creation of multiple virtual instances of a single physical server using specialized software. Each virtual server functions independently, with its own operating system and applications, effectively dividing the physical server's resources. This approach leads to efficient use of server resources, resulting in cost savings, better scalability, and easier management.
The technology operates through a software layer called a hypervisor, which is positioned between the hardware and the operating system. The hypervisor abstracts the physical resources, such as CPU, memory, and storage, and dynamically allocates them to various virtual machines (VMs). These virtual machines run their own operating systems and applications, enabling the hosting of multiple environments on one physical server.
Is Server Virtualization Right for Your Business?
Server virtualization consolidates multiple operating systems (OS) on a single server. Consider it if you need to do any of the following:
- Use more applications and OS without breaking budgets for hardware, electricity, and space.
- Reduce the hours that IT staff spend on installing, patching, administering, and supporting applications servers.
- Add storage virtualization to reduce application downtime and simplify backup.
- Master cloud challenges. Having experience with virtual servers will prepare your business for migrating other business-critical services to the cloud.

Virtualization is a process that entails more than purchasing and installing a product
Server virtualization can be viewed as part of an overall virtualization trend in enterprise IT that includes storage virtualization, network virtualization, and workload management. This trend is one component in the development of autonomic computing, in which the server environment will be able to manage itself based on perceived activity. Server virtualization can be used to eliminate server sprawl, to make more efficient use of server resources, to improve server availability, to assist in disaster recovery, testing and development, and to centralize server administration.