Network Virtualization

Network virtualization (NV) is defined by the ability to create logical, virtual networks that are decoupled from the underlying network hardware to ensure the network can better integrate with and support increasingly virtual environments. Over the past decade, organizations have been adopting virtualization technologies at an accelerated rate. Network virtualization (NV) abstracts networking connectivity and services that have traditionally been delivered via hardware into a logical virtual network that is decoupled from and runs independently on top of a physical network in a hypervisor. Beyond L2-3 services like switching and routing, NV typically incorporates virtualized L4-7 services including firewalling and server load-balancing. NV solves a lot of the networking challenges in today’s data centers, helping organizations centrally program and provision the network, on-demand, without having to physically touch the underlying infrastructure. With NV, organizations can simplify how they roll out, scale and adjust workloads and resources to meet evolving computing needs.
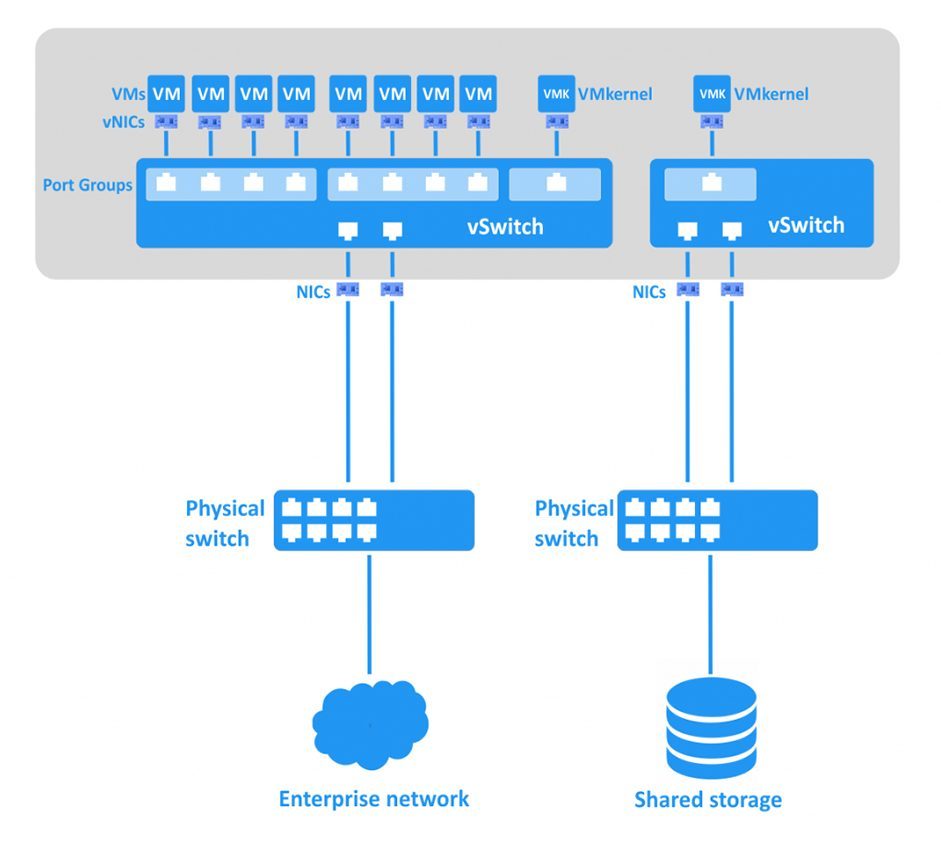
With virtualization, companies can take advantage of the efficiencies and agility of software-based compute and storage resources. While networks have been moving towards greater virtualization, it is only recently, with the true decoupling of the control and forwarding planes, as advocated by software-defined networking (SDN) and network functions virtualization (NFV), that network virtualization has become more of a focus.
Applying virtualization to the network
When applied to a network, virtualization creates a logical software-based view of the hardware and software networking resources (switches, routers, etc.). The physical networking devices are simply responsible for the forwarding of packets, while the virtual network (software) provides an intelligent abstraction that makes it easy to deploy and manage network services and underlying network resources. As a result, NV can align the network to better support virtualized environments.
Virtual networks
NV can be used to create virtual networks within a virtualized infrastructure. This enables NV to support the complex requirements in multi-tenancy environments. NV can deliver a virtual network within a virtual environment that is truly separate from other network resources. In these instances, NV can separate traffic into a zone or container to ensure traffic does not mix with other resources or the transfer of other data.

VMware network virtualization and VMware NSX
A virtual network built with VMware NSX is a software container that offers logical network pieces to connected workloads.
VMware NSX Data Center is a network virtualization platform, delivering networking and security entirely in software, abstracted from underlying physical infrastructure. NSX uses software to provide networking functions like fire-walling, switching, and routing. This means that multiple users can share the same physical environment using virtual networks invisible to each other to increase efficiency and security.
These logical networks are created and managed programmatically by using the underlying physical network as a packet forwarding backplane, allowing for network and security servers to be appropriated and attached to virtual machines (VMs) within a network. As the VM moves from host to host, these services will remain attached to it and go where it goes. VMware says its network virtualization can help data center operators achieve better speed, economics, and choice.
Use cases for NSX data center
Micro-segmentation
Reduce your attack surface by bringing micro-segmentation and intrinsic security to applications built on VMs, containers, or bare metal servers, in private and public cloud environments.
Network Automation
Increase speed and agility by automating networking and security services entirely in software, empowering IT and developers to move at the speed of business by treating network infrastructure as code.
Multi-Cloud Networking
Streamline networking and security operations by bringing consistency across, data center, private clouds, and public clouds including AWS and Azure.
Cloud-Native Apps
Deliver native networking and security for containerized workloads that brings consistent and automated policy across application frameworks, platforms, sites, and clouds.
VMware network virtualization benefits
Agility
Cost
Choice
Network virtualization can be categorized as either external or internal. External network virtualization is the combining of one or more local networks or parts of networks into a whole “virtual” network with the intended goal of improving the efficiency of a large network or data center. Its two key components are the virtual local area network (VLAN) and the network switch. Using these two together, system administrators can configure systems that are physically attached at the same local network into many different virtual networks.